Discrete Vector Field Topology¶
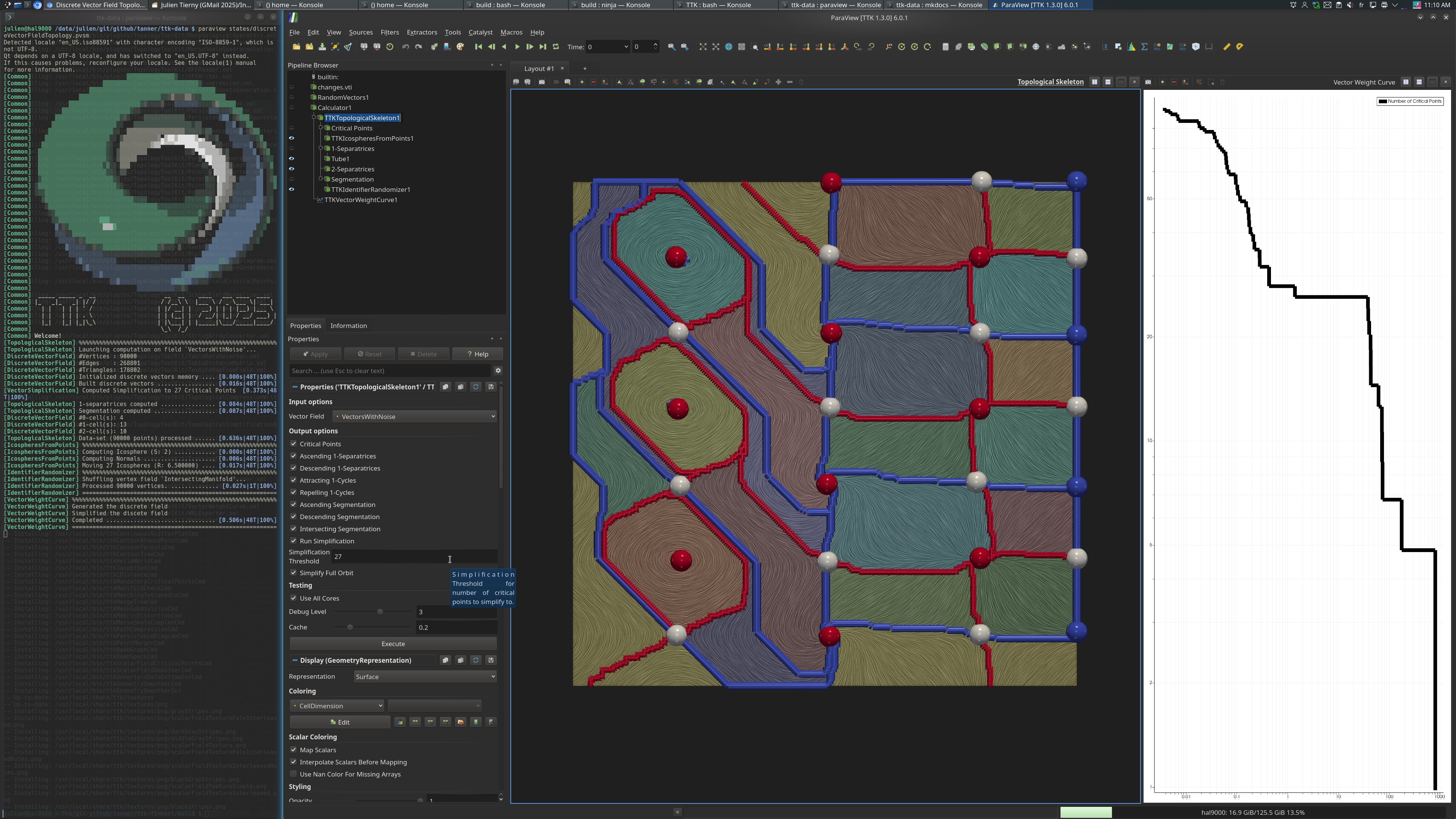
Pipeline description¶
This example computes the critical points, separatrices, and segmentation of a simplified vector field with added noise and threshold determined by the associated weight curve.
First, the vector field data is added with a random vector of size 0.3.
Then, the VectorWeightCurve is computed. The output is the simplified pairs and the weight associated with each pair. We use this curve to determine stable/flat regions to simplify to. Looking at the displayed weight curve (using log scales), we see a good (flat) spot to simplify to at 27 critical points.
Next, the input data is simplified based on the selected threshold (27 critical points), via TopologicalSkeleton and using VectorSimplification on the backend.
Finally, the Critical Points and Separatrices are computed then displayed and
the Intersecting Manifold segmentation is shown (with a random color per
manifold, by using IdentifierRandomizer).
ParaView¶
To reproduce the above screenshot, go to your ttk-data directory and enter the following command:
paraview states/discreteVectorFieldTopology.pvsm
Python code¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | |
To run the above Python script, go to your ttk-data directory and enter the following command:
pvpython python/discreteVectorFieldTopology.py
Inputs¶
- changes.vti: a two-dimensional regular grid encoding flow of a piecewise implicit function.
Outputs¶
WeightCurve.csv: the plot of pairs according to weight and total number of critical points remaining in the simplified field.CriticalPoints.csv: the critical points of the simplified DiscreteVectorField.Separatrices1.csv: the output separatrices traced along the saddles (critical simplices of dimension 1) on the simplified field.Segmentation.vtu: the output segmentation in VTK file format. The segmentation is stored as point data with segment numbers associated with common flow patterns (descending, ascending, and intersecting).